Before getting into today's topic, I'd recommend you read my previous two articles on protein if you haven't already. You can find Part 1 here and Part 2 here.
Speed of absorption
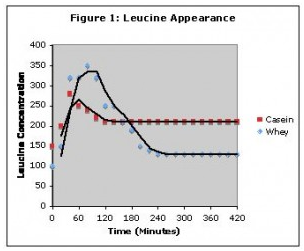
We all know that whey protein is the fastest digesting protein there is and casein is the slowest. That's why we drink whey protein after we workout and casein before bed... right? If you know me well enough, then you know I was setting you up. The correct answer is, "not exactly". Look at this graph pulled from The Protein Book.
The Protein Book - Lyle McDonald
One thing you should notice is that whey and casein hit the bloodstream at the same time. The difference is not that whey spiked blood amino acid levels faster but instead, whey spiked them higher than casein. The other thing you should notice is that with whey protein, the blood amino acid levels fell much faster as well.
Note: The above graph was based on the 1997 Boirie Study titled, Slow and fast dietary proteins differently modulate postprandial protein accretion.” In the study, participants were given either whey or casein after a morning fast. No other macronutrients were consumed with the protein. The results of the study wouldn't necessarily be as the graph depicts them if other macronutrients had been consumed in conjunction with the protein.
It would be beneficial to take a moment to explain the different possibilities for increasing muscle size.
- One way would be to increase muscle synthesis. Synthesis is where small structures combine to make larger ones.
- The other way would be to decrease muscle breakdown. Breakdown is where large structures are broken down into smaller ones.
- The third option would be to do both.
The Boirie study also looked at the effects of the two different types of protein. The study found that whey increased protein synthesis but did not affect protein breakdown. Conversely, the study found that casein decreased protein breakdown but did not affect protein synthesis. This means that whey was found to be anabolic (synthesizes protein) and casein was found to be anti-catabolic (prevents protein breakdown).
There you have it! Whey protein is anabolic. That means whey protein is better, right? Well, again, not exactly. The study showed that casein caused the participants to store more leucine (Leucine is a branched chain amino acid used here as an indicator of what the other amino acids are doing). From this one could draw the conclusion that preventing protein breakdown is more important than promoting protein synthesis.
Oh, I get it now. Casein is better! Well, yet again, not so fast. In the Biori study, the leucine content of each group was equated. Whey and casein have different leucine concentrations; therefore, the casein group was actually given more total protein. A follow-up study was conducted that used mixed meals and also equated the amount of whey and casein given to each group. In this study, the whey group actually pulled out ahead, although not by much. Also, when previous meals are still digesting, the speed of absorption is affected. A fast digesting protein won't be so fast if there is already food in your system being digested. For the record, a combination of both whey and casein seems to be better than either in isolation.
Here is a table that shows the absorption rate of other types of protein as well.
The protein book - Lyle McDonald
I had actually planned on this being the last installment in the protein series but I want to keep this going until I tie up all the loose ends. If you're interested in purchasing some whey or casein protein, I've provided some affiliate links below.
Optimum Nutrition 100% Gold Standard Whey
Optimum Nutrition 100% Gold Standard Casein
Dymatize Nutrition Elite Whey Protein
Dymatize Nutrition Elite Casein Protein
Don't forget to like, share, and comment on social media. Thanks for reading and God Bless!